Supported MySQL Data Types in different versions
May 21st, 2020,
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system, founded by MySQL AB in 1995. It inspired the development of MariaDB, and is also used in many popular websites and many database-driven web-applications. Developers tend to use MySQL generally for the following reasons:
• It’s available on many system platforms ;
• It’s available on both proprietary and GPL licenses ;
• It has an important support community ;
• Oracle offers paid support for MySQL server ;
• Developers interfaces are available and sometimes included with the server download package ;
• Well explained documentation ;
• Positive reviews about performance, stability, multi-users and multi-threading ;
This article studies the evolution of data types support from the version 3.23.31 (January 17th, 2001) to the actual one (8.0.16, April 25th, 2019). The first production release is the 3.21 version (1998), but there is no necessarily official information about this latter. Consequently, we are going to survey the first production (general availability) minor version for each innovating major version of MySQL. By innovation, we mean version of MySQL which added new data types, new synonyms or notified some changes about them.
| Version release | 3.23.31 | 4.1.7 | 5.1.30 | 5.5.8 | 5.7.9 | 8.0.16 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numeric Types | Integer Types | TINYINT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| SMALLINT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| MEDIUMINT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| INT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| INTEGER | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| BIGINT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| SERIAL | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Fixed Point Types | NUMERIC | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| FIXED | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| DEC | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| DECIMAL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Floating Point Types | FLOAT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| DOUBLE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| REAL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| DOUBLE PRECISION | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Bit Value Types | BIT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| BOOLEAN | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| BOOL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Date and Time Types | DATE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| DATETIME | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| TIMESTAMP | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| TIME | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| YEAR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| String Types | CHAR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| NATIONAL CHAR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| VARCHAR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| NATIONAL VARCHAR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| BINARY | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| VARBINARY | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| BLOB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| TINYBLOB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| MEDIUMBLOB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| LONGBLOB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| TEXT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| TINYTEXT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| MEDIUMTEXT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| LONGTEXT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| ENUM | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| SET | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Spatial Types | No | No | Partial | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| JSON | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | ||
| Supported Data Types Number | ||||||||
The first version of MySQL (v. 3.23.31; January 17th, 2001) was supporting both of numeric, string and date and time (date and time) data types. Numeric ones included integers (TINYINT, SMALLINT, MEDIUMINT, INT and BIGINT), fixed-point (DECIMAL), float-point (FLOAT and DOUBLE) and bit values (BIT). String data types included CHAR, VARCHAR, TINY BLOB, TINYTEXT, BLOB, TEXT, MEDIUMBLOB, MEDIUMTEXT, ENUM and SET.
Date and time data types included DATE, DATETIME, TIMESTAMP, TIME and YEAR ones. In the other hand, the version 3.23.31 of MySQL supports the synonyms BOOL (for TINYINT(1)), INTEGER (for INT), DEC and NUMERIC (for DECIMAL), DOUBLE PRECISION and REAL (for DOUBLE).
Then, the version 4.1.7 appeared on October 23rd, 2004. It supported new data types that are BINARY and VARBINARY, and new synonyms which are SERIAL (for BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT UNIQUE), BOOLEAN (for TINYINT(1)) and FIXED (for DECIMAL). In addition of that, the BIT data type in the MySQL version 3.23.31 became also a synonym for TINYINT(1) (just like BOOL and BOOLEAN) in the version 4.1.7. Later, the version 5.0.15 of MySQL came out on October 19th, 2005. It changed the BIT synonym into a particular data type accepting a length to 64 bits.
After that came the version 5.1.30 on November 14th, 2008. It included mostly the spatial data types (like POINT, POLYGON, LINESTRING …). Next, the version 5.5.8 came out on December 3rd, 2010. It added the rest of the spatial data types supported until now (like CURVE and SURFACE). At the end, the version 5.7.9 of MySQL came out on October 21st, 2015. It added a native data type for JSON values.
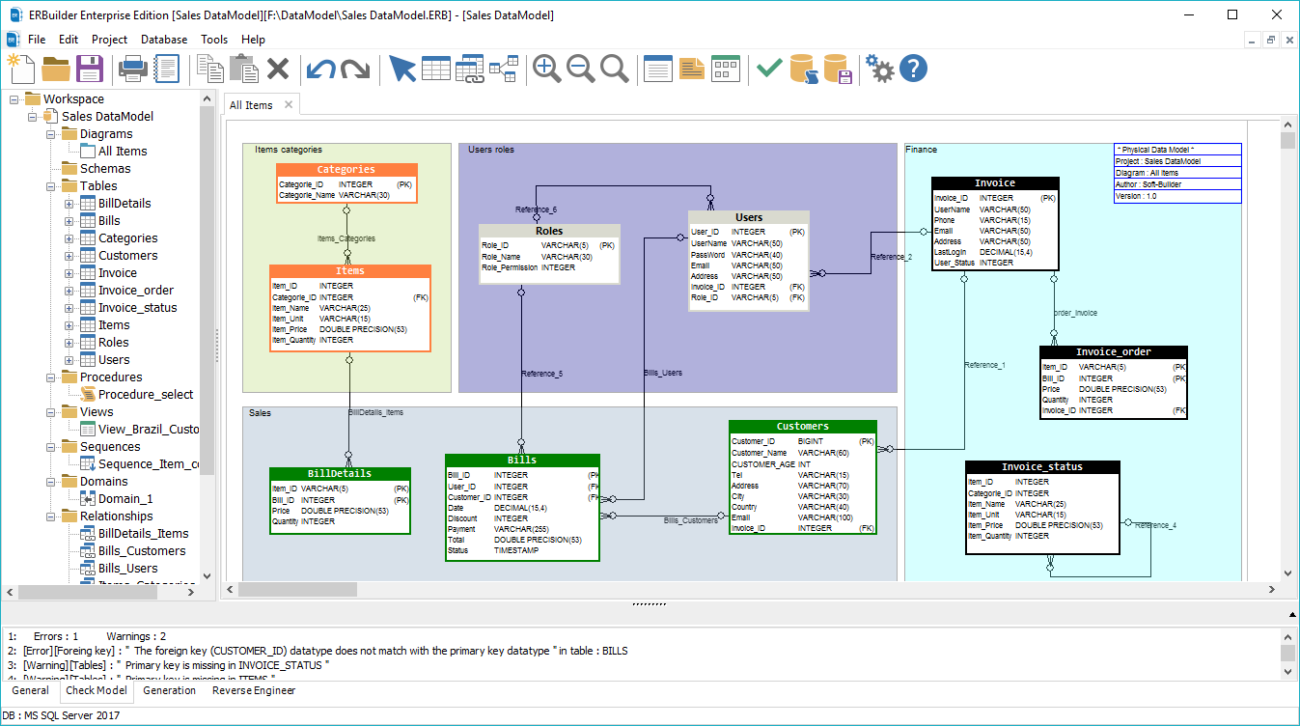
ERBuilder is a GUI data modeling tool that allows you to visualize, design and model MySQL databases(and others) by using entity relationship diagrams and automatically generates the most popular SQL databases. Generate and share the data Model documentation with your team. Optimize your data model by using advanced features such as test data generation, schema compare and schema synchronization. Try now ERBuilder for 15 days FREE
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Subscribe to our email newsletter today to receive updates of the latest news, tutorials and special offers!
Share on:
See also
- Schema synchronization has arrived in ERBuilder 3.4
- Odoo Database Model